![[*]](crossref.png) .
.
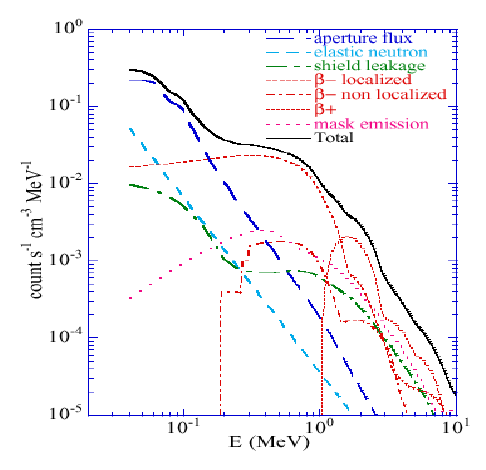
The continuum background can be split into several components,
depending on their origin. On the one hand, the radiation coming from outside the
instrument. This can be the cosmic diffuse gamma ray flux that comes
in through the instrument aperture, or leakage through the BGO shield
of cosmic diffuse gamma ray radiation and gamma continuum radiation
from the spacecraft (induced by energetic cosmic ray particles).
On the other hand, scattering in the germanium detectors of neutrons that were
produced in the spacecraft or other parts of the instrument. Finally,
there are background components produced inside the spectrometer detectors.
These consist of localized
decays, non localized
decays and
decays. The continuum emission from
the mask and the BGO emission when the veto electronics are blacked
out (veto dead time) are negligible. The individual components and
the total continuum background emission are illustrated in Figure
![[*]](crossref.png) .
.
 |